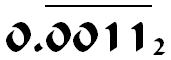Basic Answers
Why don’t my numbers, like 0.1 + 0.2 add up to a nice round 0.3, and instead I get a weird result like 0.30000000000000004?
Because internally, computers use a format (binary floating-point) that cannot accurately represent a number like 0.1, 0.2 or 0.3 at all.
When the code is compiled or interpreted, your “0.1” is already rounded to the nearest number in that format, which results in a small rounding error even before the calculation happens.
Why do computers use such a stupid system?
It’s not stupid, just different. Decimal numbers cannot accurately represent a number like 1/3, so you have to round to something like 0.33 - and you don’t expect 0.33 + 0.33 + 0.33 to add up to 1, either - do you?
Computers use binary numbers because they’re faster at dealing with those, and because for most calculations, a tiny error in the 17th decimal place doesn’t matter at all since the numbers you work with aren’t round (or that precise) anyway.
What can I do to avoid this problem?
That depends on what kind of calculations you’re doing.
- If you really need your results to add up exactly, especially when you work with money: use a special decimal datatype.
- If you just don’t want to see all those extra decimal places: simply format your result rounded to a fixed number of decimal places when displaying it.
- If you have no decimal datatype available, an alternative is to work with integers, e.g. do money calculations entirely in cents. But this is more work and has some drawbacks.
Why do other calculations like 0.1 + 0.4 work correctly?
In that case, the result (0.5) can be represented exactly as a floating-point number, and it’s possible for rounding errors in the input numbers to cancel each other out - But that can’t necessarily be relied upon (e.g. when those two numbers were stored in differently sized floating point representations first, the rounding errors might not offset each other).
In other cases like 0.1 + 0.3, the result actually isn’t really 0.4, but close enough that 0.4 is the shortest number that is closer to the result than to any other floating-point number. Many languages then display that number instead of converting the actual result back to the closest decimal fraction.
© Published at floating-point-gui.de under the Creative Commons Attribution License (BY)